What does a CFO do?
The Chief Financial Officer (CFO) is the highest-level financial manager in a company. They have many roles and responsibilities that influence a company's success.
The position of Chief Financial Officer (CFO) is the highest-level financial management position in a company. CFO responsibilities focus primarily on overseeing the financial health and activities of a business or organization. A CFO is responsible for the short-term and long-term financial growth of a company, including financial planning, risk management, recordkeeping, financial reports, and, often, data analysis.
In addition to overseeing the company’s day-to-day cash flow, the CFO also makes decisions regarding a company’s capital structure (the company’s combination of equity and debt) and ensures that the company receives the best return possible.
The CFO’s primary goal is to help make decisions that increase revenue and ensure the company has a healthy cash flow and spends its capital well. Among a CFO’s many responsibilities is compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. He may also forecast and develop long-term plans for a company's profitability. A CFO prepares financial reports and may directly or indirectly supervise staff members who perform financial tasks.
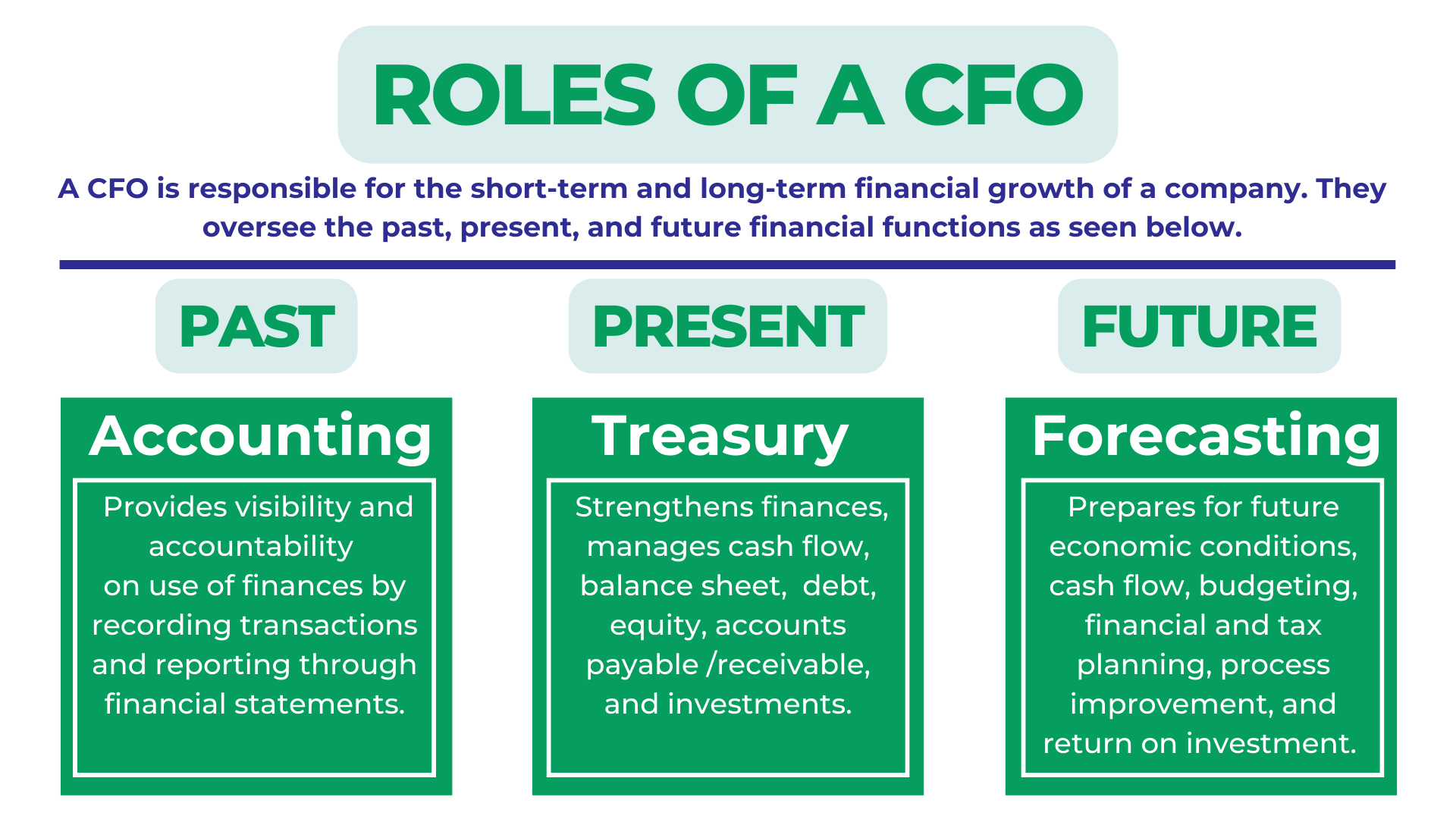

Company finances generally fall into three main categories: accounting, treasury functions, and forecasting. These deal with the past, present, and future of a company, and a CFO oversees all three areas.
- Accounting: Accounting is headed by a controller, and includes maintaining accounting records, income, expenses, payroll, inventory, compliance, and producing financial reports.
Accounting is the process of systematically recording, analyzing, and interpreting the business’s financial information. Business owners use accounting to track their financial operations, meet legal and tax obligations, and make stronger business decisions. Accounting is recording and evaluating what happened in the past.
- Treasury: Treasury management includes overseeing financial reserves, liquidity, debt, risk, capital structure, equity and internal financing, cash flow, accounts payable and receivable, inventory, etc.
The purposes of treasury finances are to optimize the organization’s liquidity, make sound financial investments, mitigate financial risks, and provide cash, interest, and investment reporting.
The treasury function manages the company’s cash and balance sheet. It is responsible for managing liquidity through funding and investments as well as financial risks. These risks include debt servicing (payments), interest, extending credit to customers, foreign exchange, commodity, insurance and pension risk. It is also responsible for managing banking relationships.
Treasury finance focuses on the present state of the company, and making the best decisions now to benefit the company in the future.
- Forecasting: Forecasting is focused on economic strategy and includes budgeting, financial planning and analysis, return on investments, future cash flow, projections, analytics and decision making, process improvement, operational excellence, identifying portions of the company making the most money, and growth and profitability constraints. It is the planning and vision for the future of the company.
A CFO must identify areas currently making a profit and areas that will continue to make a profit in the future. Preparing the business to meet future economic, tax, and regulatory conditions and opportunities can make the difference between surviving and growing or going out of business laden with debt and distress.
Identifying sound investments and proper diversification of resources both internal and external is of significant importance to ensuring company profitability and long term success.
The CFO coordinates with the chief executive officer (CEO) on tax planning strategies and regulatory environments. They also provide input to the CEO for corporate legal counsel and the board of directors on entity structures and succession planning.
Does your company need help with financial functions? Schedule a free consultation today!
Responsibilities of a CFO
Financial Management:
When major financial decisions or initiatives arise, the CFO is responsible for being the regulatory agent, analyzing the risks, and helping the CEO make decisions. Corrective actions, process improvement in response to financial weaknesses and prioritizing are all tasks related to this responsibility.
Financial Strategy:
In addition to managing the company’s current finances, the CFO is responsible for the long-term financial strategy of the company in coordination with the chief executive officer (CEO) and board of directors.
A CFO partners with the CEO to develop long-term plans for the business including investments and capital planning. When the company wants to undertake a costly new venture, the CFO is responsible for making sure the resources are available to implement the plan. This task involves cash flow management, budget development and assessment of financial strengths and weaknesses.
CFOs are decision-makers responsible for analyzing financial reports to assist the management team in making the most informed decisions possible. They should be able to review all the data and statistics available in order to make final financial decisions for the company. Departmental oversight—including budgets, statements, and account management—may all come directly from the CFO’s office. Capital structure, managing income, managing expenses, and more are all related to regular financial management.
Cultivating Relationships with Financers:
CFOs are often responsible for finding additional funding sources and establishing connections with banks, investors, and other lenders to ensure the organization’s finances are secure and stable.
A CFO is an ambassador who facilitates financial discussions with other parties inside and outside the company. They are an authority on the financial state of the company, so credibility is critical to the organization's success. A CFO may be involved in negotiations for large contracts with customers and vendors. The CFO works closely with different C-level positions in the company, including the Chief Executive Officer (CEO), the Chief Information Officer (CIO), the Chief Product Officer (CPO), the Chief Operating Officer (COO), and the Chief Marketing Officer (CMO), to determine strategies for budget management, product pricing, and investments.
Reporting:
One of the primary duties of CFO is to report on and present the financial condition and outlook of the company. They prepare financial statements for shareholders, creditors (such as lending institutions) and analysts.
The CFO is also responsible for ensuring the company adheres to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and follows all laws and regulations regarding financial reporting, disclosures, and taxes. The CFO must stay informed of the company’s financial information and what money-related decisions are on the horizon. The CFO serves as a financial analyst who collects data and crunches numbers to create budgets, conducts cost-benefit analysis, predicts future financial decisions or hiccups, and mitigates financial risk.
At the end of the day, the CFO’s objective is to optimize financial performance, mitigate risk, and ensure maximum profit for the company they lead.
At Crescendo Now we get that the financial strategy of your business is vital. That is why we are here to help! In addition to accounting and data analytics services, we offer CFO advising so you can optimize your finances. We’d love to chat about how Crescendo Now can help your business grow and succeed. Schedule a free consultation today or learn more about what we have to offer!
No comments yet. Login to start a new discussion Start a new discussion